At The Sims Law Firm, we know that understanding the complexities of theft laws in Mississippi can be daunting. Our firm serves as your guide to these legal classifications, where offenses are categorized based on the value of stolen property and the specific circumstances under which the crime was committed. This comprehensive guide delves into the various classifications of theft charges, providing you with a thorough understanding of theft-related offenses in the state.
Classifications of Theft Crimes in Mississippi
Petty Larceny and Grand Larceny
In Mississippi, the distinction between petty larceny and grand larceny hinges on the value of the stolen items. Petty larceny includes items valued under $1,000, leading typically to misdemeanor charges, which are generally less severe and may involve fines or short jail terms. In contrast, grand larceny concerns items valued over $1,000 and is considered a felony with more severe consequences.
As per Mississippi Code Section 97-17-41, the penalties for grand larceny escalate with the value of the stolen property. The theft of property worth between $1,000 and $5,000 can lead to up to five years in prison, while stealing more than $25,000 could result in up to twenty years of incarceration. These laws reflect the state’s stance on increasingly punitive measures for higher-value thefts, emphasizing the seriousness with which property crimes are treated.
Robbery
Robbery in Mississippi is defined under Mississippi Code Section 97-3-73 as the direct taking of property from a person through intimidation or force. Unlike theft, which may or may not involve direct contact with the victim, robbery always involves confrontation and is considered a violent crime, leading to harsher penalties.
The law specifies that robbery, especially armed robbery, is treated with significant severity, recognizing the potential physical harm to victims. Penalties for robbery can extend to long-term imprisonment, reflecting the dual nature of the crime involving both theft and assault.
These classifications are crucial for understanding how theft charges are approached in Mississippi’s legal system. Each category is defined not only by the value of the property involved but also by the manner in which the crime is executed, impacting the legal proceedings and penalties that follow. This structured approach to categorizing and penalizing theft crimes plays a key role in the state’s criminal justice system, aiming to proportionately punish and deter such offenses.
For more insights into specific cases and detailed legal discussions on theft and robbery in Mississippi, further exploration of state statutes and case law is invaluable. This foundational knowledge assists in navigating the complexities of criminal charges and understanding the potential legal consequences faced by individuals charged with these serious offenses.
Burglary
Burglary in Mississippi is defined as the unlawful entry into a building with the intent to commit a crime, most often theft. This crime is codified under Mississippi Code Section 97-17-33, which delineates the nuances of how burglary charges are approached depending on various factors. The severity of burglary charges can escalate based on whether the entry was into a dwelling, which typically results in harsher penalties, and whether the burglar was armed, which can elevate the charge to aggravated burglary.
For example, the mere act of breaking and entering does not constitute burglary unless it is accompanied by the intent to commit a crime inside. Moreover, if the burglary occurs at night or the offender possesses explosive or dangerous weapons, the penalties increase significantly, reflecting the increased potential threat to personal safety.
Shoplifting
Shoplifting is specifically addressed with detailed penalties in Mississippi under Mississippi Code Section 97-23-93. This statute categorizes shoplifting charges based on the retail value of the stolen items and the offender’s prior convictions. For first-time offenders, penalties may be relatively mild, but for individuals with prior convictions, the consequences become substantially more severe, including possible felony charges for high-value items. This progressive penalty system aims to deter repeat offenders and reduce shoplifting incidents, which can significantly impact local businesses.
Receiving Stolen Property
Possession of known stolen property is another serious theft offense in Mississippi, governed by Mississippi Code Section 97-17-70. The severity of the charge and corresponding penalties are determined by the value of the stolen property. For property valued under $1,000, the offense is treated as a misdemeanor, but as the value increases, so does the gravity of the charge, potentially reaching felony status for high-value items. This law underscores the responsibility individuals have to ensure they are not in possession of stolen goods and reflects the state’s commitment to curbing the circulation of unlawfully obtained property.
These statutes collectively contribute to a robust legal framework designed to address various forms of property crimes, from unlawful entry and theft in a dwelling to the deceitful possession of stolen goods. Understanding these laws is crucial for anyone involved in or affected by property crimes in Mississippi, offering insights into potential legal implications and the importance of lawful behavior concerning property ownership and integrity.
Theft Crime Statistics in Mississippi
The current state of theft crimes in Mississippi is detailed through crime statistics that shed light on the frequency and context of these offenses. According to the Mississippi Crime Statistics, in 2023, there were nearly 36,000 incidents of property crime across the state. Here’s a breakdown of those crime numbers, along with a matching pie chart (created by The Sims Law Firm) that shows each type of property crime as percentage of all property crimes in Mississippi:
| All Property Crimes | Robbery | Larceny – Theft | Burglary | Fraud | Embezzlement | Extortion – Blackmail | Motor Vehicle Theft | Arson |
| 35,987 | 478 | 20,986 | 6,043 | 4,699 | 701 | 52 | 2,880 | 148 |
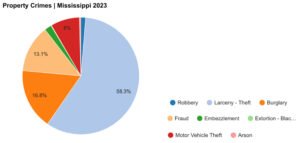
Distribution of theft crimes in Mississippi for 2023
FAQs About Theft Charges in Mississippi
Can Theft Charges Be Dropped in Mississippi?
Yes, theft charges may be dropped due to insufficient evidence, restitution agreements, or through pre-trial diversion programs for first-time offenders.
Can Theft Charges Be Expunged in Mississippi?
Certain theft charges, particularly misdemeanors or first-time offenses, can be expunged from an individual’s record under guidelines set forth in Mississippi Code Section 99-19-71, depending on the circumstances and the crime’s nature.
What Happens When Theft Charges Are Filed?
The process typically begins with an arraignment, followed by possible bail hearings, pre-trial motions, and the trial itself where evidence is presented by both prosecution and defense.
Can Misdemeanor Theft Charges Be Dropped?
Like any theft charge, misdemeanor charges can be dropped if there is insufficient evidence, or if terms such as restitution or community service are negotiated successfully.
Don’t Face Theft Charges Alone: Get the Defense You Deserve
The different types of theft and their penalties in Mississippi can be confusing. To avoid getting lost in the legal system, a strong grasp of the relevant laws is essential. At The Sims Law Firm, Trae Sims is dedicated to providing robust defense strategies and ensuring the best outcomes for his clients. Learn more about legal representation and services offered by The Sims Law Firm, by exploring our about page. For more insights into Mississippi law, check out our blogs section. To schedule a free consultation, visit our contact page, email, or call us at (601) 207-3732.
List of References
- Mississippi Property Crime Statistics – 2023
- List of Mississippi Statutes – Felony vs. Misdemeanor Classifications
- Mississippi Code Section 97-17-41
- Mississippi Code Section 97-3-73
- Mississippi Code Section 97-17-33
- Mississippi Code Section 97-23-93
- Mississippi Code Section 97-17-70
- Mississippi Code Section 99-19-71






